Wu and Carson [1] aimed at making the SRTM basis function approach even more robust and called it Simplified Reference Tissue Model 2 (SRTM2). They noted that with SRTM k2' is calculated with each pixel TAC, although the same reference TAC is used for all pixels. Therefore they implemented a two-step approach:
The operational equation of the SRTM was re-written to allow for fixing of k2'. This is relevant for parametric mapping because the model in each pixel TAC uses the same reference TAC and therefore should employ the same k2'. Defining the ratio of tracer delivery R1 as K1/K1' and the binding potential BPND as k3/k4, the following operational equation can be derived for the measured TAC in a receptor-rich region:
![]()
The three unknowns R1, k2 and k2a in this equation can be fitted using nonlinear regression techniques. The binding potential can then be calculated as
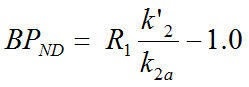
The PXMOD implementation BPnd (Wu SRTM2 Ref) differs from that described in [1] in the following points
Acquisition and Data Requirements
Image Data |
A dynamic PET data set with an neuroreceptor tracer which behaves kinetically similar to a 1-tissue compartment model. |
TAC 1 |
TAC from a receptor-rich region (such as basal ganglia for D2 receptors). |
TAC 2 |
TAC from a receptor-devoid region (such as cerebellum or frontal cortex for D2 receptors). |
Model Preprocessing
Two regional TACs (TAC1 and TAC2) are needed for Model Preprocessing.
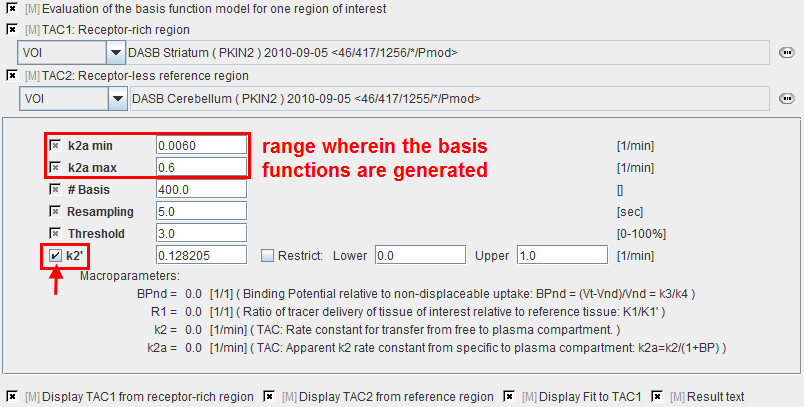
k2a min |
Minimal value of k2a (slowest decay of exponential). |
k2a max |
Maximal value of k2a (fastest decay of exponential). |
# Basis |
Number of basis functions between k2a min and k2a max. Note that increments are taken at logarithmic steps. This number is directly proportional to processing time. |
Resampling |
Specifies the interval of curve resampling which is required for performing the operation of exponential convolution. Resampling should be equal or smaller than the shortest frame duration. |
Threshold |
Discrimination threshold for background masking. |
k2' |
k2 of the reference tissue. It can be fixed at a specified value, or fitted. If it is checked, k2' is fitted using the SRTM method implemented in PKIN. This value will be used in pixel-wise SRTM2. |
BPnd |
Estimated binding potential (= k3/k4 according to the underlying model). |
R1 |
Ratio of tracer delivery in each pixel relative to the reference tissue (R1=K1/K1'). |
k2 |
Estimated rate constant k2. |
k2a |
k2a value which provides the best least squares fit in each voxel. |
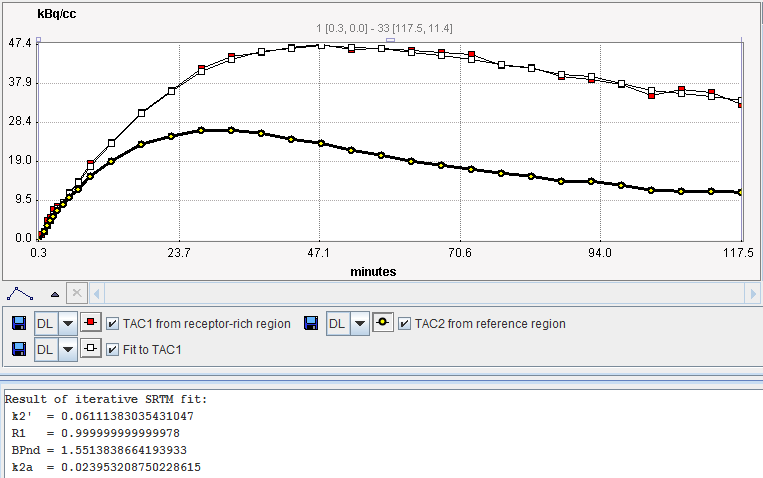
The result of the fit during Model Preprocessing is shown in the Result panel for inspection.
Model Configuration
BPnd |
Estimated binding potential (BPnd= k3/k4 according to the underlying model). |
k2 |
Estimated efflux rate constant k2 . |
R1 |
Ratio of tracer delivery in each pixel relative to the reference tissue (R1=K1/K1'). Therefore the map often has a similar appearance to a perfusion image. |
k2a |
k2a value which provides the best least squares fit. |
Note: The k2a parametric map should be checked in the initial setup of a processing protocol. The estimated k2a values should not be truncated by too narrow k2a min and k2a max values.
Reference
1. Wu Y, Carson RE: Noise reduction in the simplified reference tissue model for neuroreceptor functional imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2002, 22(12):1440-1452. DOI