The quick settings for the keyboard-driven definition of the Peak VOIs and iso-contouring VOIs are accessible under the Data Inspector in the VOI Settings tab as illustrated in the capture below:
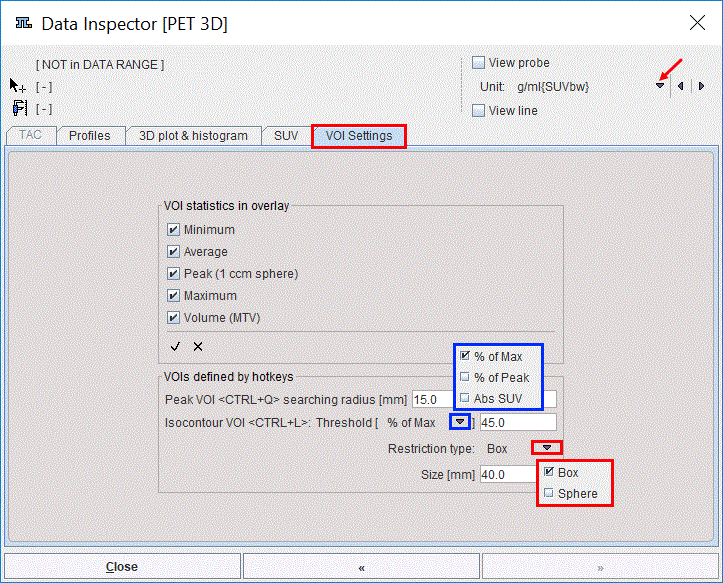
The tab is organized in two main sections: the VOIs statistics in overlay and the VOIs defined by hotkeys. Both sections are described in detail below.
VOI Statistics in Overlay
This section allows selecting/deselecting statistics measures of interest to be overlaid on to the image. The selected statistics measure of interest are the ones with checked boxes enabled. Simply click into a box for changing the selection. The task of selecting statistic measures of interest is supported by shortcuts in the bottom of the section:
|
Set the selection check of all statistics measures in overlay |
|
Remove the selection check of all statistics measures in overlay. |
VOIs Defined by Hotkeys
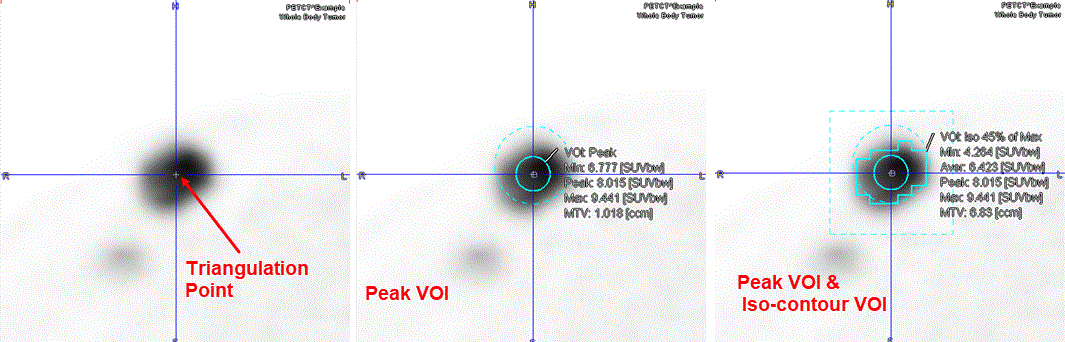
The Peak VOI and the Isocontour VOI require the definition of a parent VOI. The parent VOIs are used as boundary restrictions for the keyboard-driven definition of the Peak VOIs and isocontouring VOIs. Please note that parent VOIs center is defined by the mouse active position in the view port. It is recommended to place the parent VOIs center as much as possible in the center of the lesion. The MIP representation of the image may be used for selecting the lesion of interest.
The VOIs defined by hotkeys section allows defining the settings for the keyboard-driven definition of the:
Initially, the algorithm creates the parent sphere VOI with the predefined searching radius in [mm]. Subsequently, the 1ccm Peak sphere VOI is defined and centered in such a manner in the parent VOI that the average is maximal. The activity calculation in the Peak VOI is performed using all the voxels inside the sphere when the center of the sphere is inside the parent VOI. In the voxels which are not fully inside the Peak VOI the average value is estimated using the fraction of the pixel value corresponding to a fraction of the surface area inside the Peak VOI. Note that the algorithm will consider only Peak spheres with the center inside the parent VOI.
Initially, the algorithm creates the parent VOI which may be a Box or a Sphere of a predefined Size in [mm]. Subsequently, one of the available isocontouring threshold criteria is used to create the iso-contour VOI. There are three criteria available for the iso-contouring threshold: % of MAX, % of Peak, and the Abs SUV threshold which are summarized in the table below:
% of Max |
The maximum pixel value is calculated in the predefined parent VOI. All the pixels within the parent VOI which value is above the specified % of the estimated Max will be part of the Iso-contour VOI. |
% of Peak |
The Peak value is estimated in the predefined parent VOI. All pixels within the parent VOI which value is above the specified % of the estimated average Peak VOI will be part of the Isocontour VOI. |
Abs SUV |
All pixels within the predefined parent VOI which value is above the absolute specified value will be part of the Isocontour VOI. Please note that empty Iso-contour VOI may occur if the absolute value is higher than the maximum pixel value within the parent VOI. |
The parent VOIs will not appear as entries in the VOIs list. Multiple keyboard-driven definition for the Iso-contouring VOI can be applied to the same lesion. Each definition will result in an Iso-contour VOI which name is assigned automatically based on the threshold selection settings. The name encoding indicates the VOI type and the criteria used for the definition settings:
Note: The settings in the VOIs Settings tab are serialized. The keyboard-driven definition of the VOIs is working only on the VOIs page.
The capture below illustrates the results of a Peak VOI within a sphere of 15 mm radius and an Isocontouring VOI with a threshold of 45% of Max within a cubic box of 40 mm size for the same hot lesion. Please note the initial position of the pointer: center of the lesion.